TABLE OF CONTENTS
Prefixbox search box analytics provide an easy way to understand how your users interact with the search box and help you understand whether the configuration and data changes you are making to your search box improve the search experience or not.
The metrics are calculated daily and you can see the historical trends for each metric.
The following analytics dashboards are available in the Prefixbox Portal for all of your search boxes.
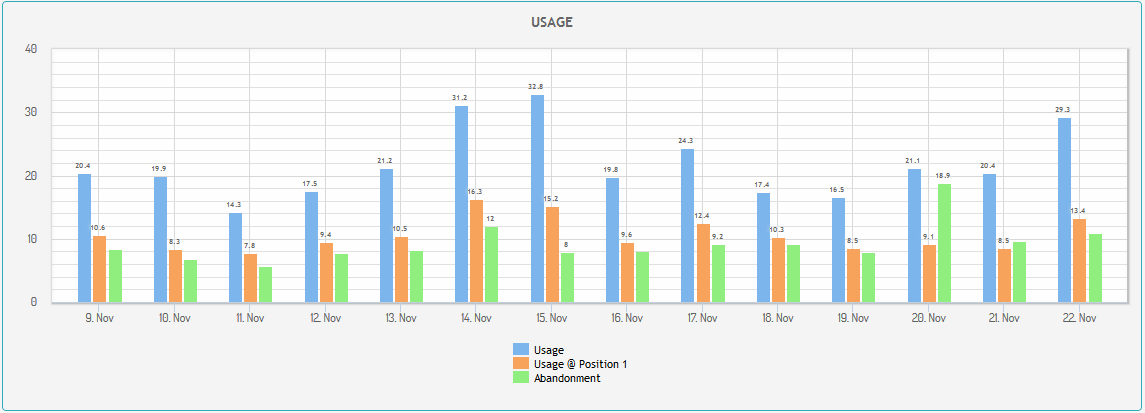
Generally speaking, we want to increase the suggestion usage and reduce the search box abandonment. Position 1 Usage gives an indication about the ranking quality of the suggestions. Our daily suggestion refresh mechanism helps you improve the suggestion usage by ranking more relevant suggestions higher automatically.
The user selected one of the suggestions when executing the search. Increasing the suggestion usage is a good thing because we can save time for the users and the Search Result Pages usually have higher quality when the users execute their searches through the suggestions.
The percentage of searches that were executed by selecting the suggestion at Position 1. The first suggestion has the highest usage among all the positions. This is known as Position Bias which is common in recommendation engines. In case of e-commerce websites we can take advantage of the Positional Bias and show certain products or product categories at higher positions to increase revenue.
The user focused into the search box but did not execute the search. High abandonment rates can indicate issues with the suggestion quality. It can also happen due to incorrect analytics tracking.

Coverage analytics help you understand how much your search box is able to show suggestions when users type and execute their searches. Conditional Usage tells you whether those suggestions were engaging to the users.
The daily suggestion list refresh helps in improving the coverage by adding more relevant suggestions to your suggestion lists based on your users’ previous searches.